JSON으로 Data를 전송해야하는 경우 쿼리를 이용하여 Table Data를 JSON타입으로 만들 수 있다.
Test Case
drop table customers;
create table customers (
customerID varchar
, customerName varchar
, contactName varchar
, address varchar
, city varchar
, postalCode varchar
, country varchar
);
insert into customers values ('1', 'Alfreds Futterkiste', 'Maria Anders', 'Obere Str. 57', 'Berlin', '12209', 'Germany');
insert into customers values ('2', 'Ana Trujillo Emparedados y helados', 'Ana Trujillo', 'Avda. de la Constitución 2222', 'México D.F.', '05021', 'Mexico');
insert into customers values ('3', 'Antonio Moreno Taquería', 'Antonio Moreno', 'Mataderos 2312', 'México D.F.', '05023', 'Mexico');
insert into customers values ('4', 'Around the Horn', 'Thomas Hardy', '120 Hanover Sq.', 'London', 'WA1 1DP', 'UK');
insert into customers values ('5', 'Berglunds snabbköp', 'Christina Berglund', 'Berguvsvägen 8', 'Luleå', 'S-958 22', 'Sweden');
insert into customers values ('6', 'Blauer See Delikatessen', 'Hanna Moos', 'Forsterstr. 57', 'Mannheim', '68306', 'Germany');
insert into customers values ('7', 'Blondel père et fils', 'Frédérique Citeaux', '24, place Kléber', 'Strasbourg', '67000', 'France');
insert into customers values ('8', 'Bólido Comidas preparadas', 'Martín Sommer', 'C/ Araquil, 67', 'Madrid', '28023', 'Spain');
insert into customers values ('9', 'Bon app', 'Laurence Lebihans', '12, rue des Bouchers', 'Marseille', '13008', 'France');
insert into customers values ('10', 'Bottom-Dollar Marketse', 'Elizabeth Lincoln', '23 Tsawassen Blvd.', 'Tsawassen', 'T2F 8M4', 'Canada');
select * from customers;
--w3schools.com에서 MySQL Database를 참조하였다.
JSON Functions
1.to_json(anyelement), to_jsonb(anyelement)
to_json(), to_jsonb 함수는 값을 json 또는 jsonb로 리턴하며, 배열과 복합체는 배열과 객체로 변환한다.
SELECT to_json('Fred said "Hi."'::text);Result : to_json (1 row) >>> "Fred said \"Hi.\""
select to_json(tmp)
from(
select customerID
, customerName
, address
, city
, postalcode
, country
from customers
) as tmp;
2.json_build_object(VARIADIC “any”), jsonb_build_object(VARIADIC “any”)
json_build_object 함수는 가변 인자 목록에서 JSON 객체를 만든다. 관례 상, 인자 목록은 키와 값이 교대로 구성된다.
SELECT json_build_object('foo',1,'bar',2);Result : json_build_object (1 row) >>> {"foo" : 1, "bar" : 2}
select json_build_object(
'customerID', customerID
, 'customerName', customerName
, 'address', address
, 'city', city
, 'postalcode', postalcode
, 'country', country
)
from customers;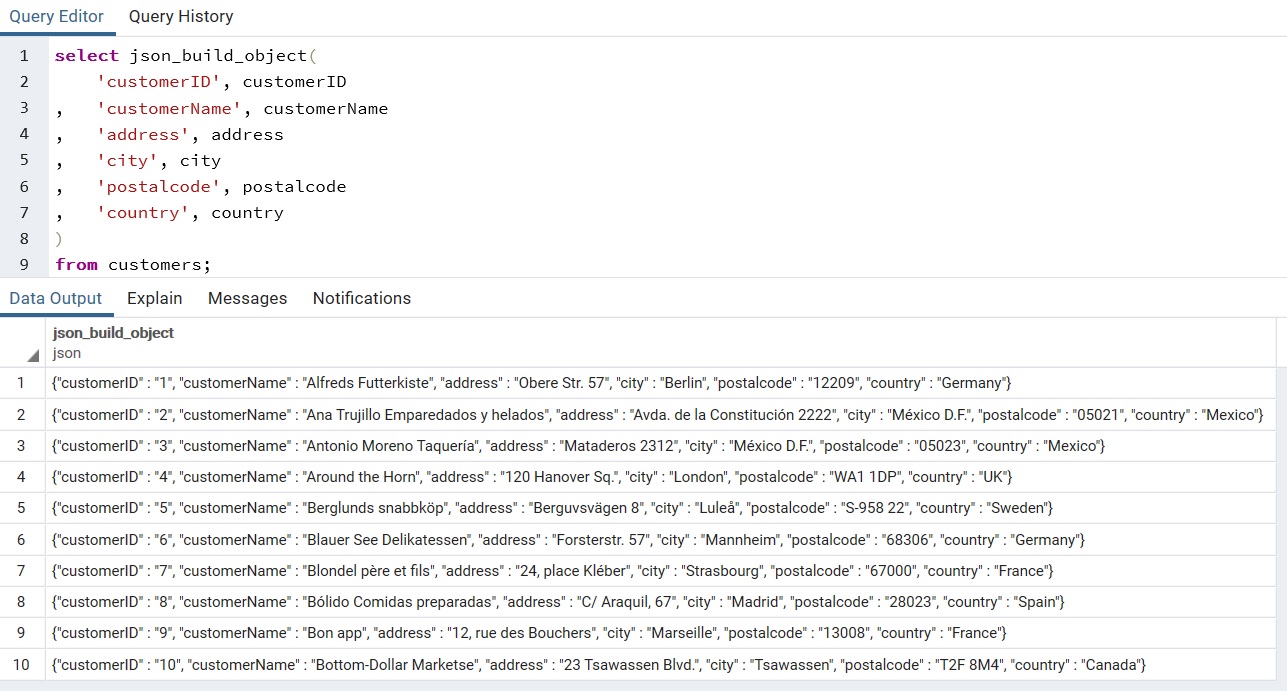
3.json_object(keys text[], values text[]), jsonb_object(keys text[], values text[])
json_object 함수는 json_object 형식에서 두 개의 개별 배열에서 키와 값을 쌍으로 가져온다. 다른 모든 측면에서 이것은 하나의 인자 형식과 동일하다.
SELECT json_object('{a, b}', '{1,2}');Result : json_object (1 row) >>> {"a" : "1", "b" : "2"}
이를 응용하여 customers table data를 응용하여 만들어 보았다.
select json_object(
array_agg('c' || customerID)
, array_agg(address || ',' || city)
) as test
from customers;
Aggregate Functions
1.json_agg(expression)
json_agg 함수는 결과의 모든 row를 값들을 모아 JSON array로 반환한다.
인자 타입 : any
반환 타입 : json
select json_agg(json_build_object(
'customerID', customerID
, 'customerName', customerName
, 'address', address
, 'city', city
, 'postalcode', postalcode
, 'country', country
))
from customers;
Reference
https://bitnine.net/documentations/manual/agens_graph_developer_manual_ko.html#sql-language
AgensGraph Developer Manual
Trapping Errors에 설명된 대로 데이터베이스 액세스에 의해 발생한 오류를 복구 하면 일부 작업이 실패하기 전에 일부 작업이 성공하는 바람직하지 않은 상황이 발생할 수 있으며, 해당 오류를 복구 한 후 데이터의 일관성이 유지된다. PL/Python은 명시적 서브 트랜젝션의 형태로 이 문제의 솔루션을 제공한다. Subtransaction Context Managers 두 계정간에 전송을 구현하는 함수를 살펴본다. CREATE FUNCTION tra
bitnine.net
'DataBase > PostgreSQL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [PostgreSQL] COALESCE 함수 (Null 체크) (1) | 2019.09.05 |
|---|---|
| [PostgreSQL] NULLIF (0) | 2019.08.13 |
| [PostgreSQL] SCHEMA CREATE, ALTER, DROP (0) | 2019.06.11 |
| [PostgreSQL] Import CSV File Into Table (0) | 2019.06.11 |
| [PostgreSQL] collate (0) | 2019.06.11 |

댓글